Everyone wants to have a massive platform for their podcast, right?
But how do you get there? What are the best ways to promote your podcast?
I’m going to try to answer that question in this blog.
How to Define Success for Your Podcast
Before you can craft a custom podcast marketing strategy you have to define what success means to your podcast.
Metrics for Podcasting Success
- Downloads and Subscribers
- Increasing Brand Recognition
- Featuring on Apple’s New and Noteworthy
- Building Community
- Entertaining listeners
- Educating Listeners
- Earning money
There are many different goals you may have for starting a podcast, and most people have more than one. It’s important to start by defining goals because it will impact the rest of your marketing decisions.
For example, if the goal for your podcast is to build brand awareness and build community, then you ought to focus on your engagement (reviews and comments on social media and YouTube).
If you are optimizing the podcast for monetization, then the number of downloads has a direct correlation to the amount of money you can make, based on the current cost per thousand (CPM) listeners of running ads.
The truth is, we see so many people start podcasts, that run for a season or less and drop off the map because they don’t see immediate ROI or growth. Growth and success of a podcast rarely happens overnight. If you want your podcast to make a big impact, you have to be dedicated to creating high-quality content and adding value. My number one encouragement for podcast marketing is to be patient.
Below I’ve listed some actionable ways for you to achieve your marketing goals, but first let’s start a basic question: what is content marketing?
What is Content Marketing?
Content marketing can include educating, entertaining, inspiring, or simply talking with your audience. It’s exactly what it sounds like: giving away free content for your audience to raise awareness for your brand, products, or services. Podcasts are a form of content marketing in and of themselves.
Content marketing is the overarching philosophy and strategy detailed in this blog. Below are strategies for how to deliver content through social media, optimize your podcast on different directories, build an email newsletter, SEO, voice search optimization, online communities, and more.
9 Podcast Marketing Strategies
- Distribution
- Episode Titles and Descriptions
- Social Media
- Podcast Website
- Email Newsletter
- Online Communities
- Guest Appearances
- Grassroots Marketing
- Paid Acquisition
1. Distribution

Podcast distribution is a crucial step in the overall marketing strategy for your podcast. There are 50+ results in the app store when you search for “podcast apps.” But the majority of listening happens on a few major platforms, including Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Google Podcasts, Audible, PocketCasts, etc.
Whenever you set up your podcast to be distributed through a hosting platform, you automatically get pushed to a lot of these directories. However, some of them require that you directly submit your podcast RSS feed. We recommend that you optimize your podcast growth strategy by putting it on as many platforms as possible, including YouTube.
Podcasting On YouTube
In addition to posting your show on all of the major (and minor) podcast directories, we recommend putting your podcast on YouTube because it opens the doors to over 2 billion monthly users.
However, the research shows that putting your podcast into a video format with a static image is not an effective way to promote your podcast. More and more podcasters are adopting the Joe Rogan format of recording a few simple static shots of their podcast. YouTube will always favor dynamic content over static images.
Learn more about how to make a video podcast here.
How to Get on Apple Podcasts New & Noteworthy
This is the million-dollar question that we seem to get asked every day: how do I get on new and noteworthy? The front page of Apple podcasts is treasured real estate, and for good reason, Apple has historically cornered the podcast market.
The first thing to acknowledge is that nobody has a 100% definitive plan to offer for how to get featured by Apple. However, the research seems to consistently point to several metrics used by Apple’s algorithm to determine what they share:
- Downloads
- Subscribers
- Ratings & Reviews
In addition, it has become common knowledge that you only can be featured in New & Noteworthy for the first 8 weeks after you launch. Because of the time window, and the main algorithm factors there are a number of common strategies that people use to boost the potential.
Strategies
- Drop multiple episodes at launch
- Push people to leave ratings & reviews on Apple podcasts (social media captions, intro/outro of your podcast, etc)
- Follow Buffer’s suggestion and run a giveaway or contest in exchange for podcast reviews
- Create engaging podcast cover art
- Choose the optimal podcast categories for your niche
The ultimate goal should be to serve your audience with high-quality content – and that will result in growth in downloads, subscribers, 5-star ratings, raving reviews, and will ultimately get you noticed by Apple.
Landing on New and Noteworthy would be a huge win for anyone, but I think it’s also worth noting that Apple is no longer the only major platform to be worried about. What about getting your podcast episode featured on Spotify’s podcast homepage, or getting recommended to new viewers on YouTube?
This leads to the next point: Optimizing your podcast content for podcast directories.
2. Episode Titles and Descriptions
SEO (search engine optimization) is integral to our internal marketing strategy as a company. Content marketing, paired with SEO has helped us build a large audience and drive growth. In the same way that you can optimize your websites content for Google, or your videos for YouTube, you can optimize your podcast for performance on the podcast directories.
How to Optimize Your Episode Titles and Descriptions
- Write short and engaging titles
- Write long and informative episode descriptions
- Format your episode descriptions using basic HTML for readability
- Create Episode-Specific Artwork
A good episode description should grip the reader and explain what your episode is about in the first sentence.
But it should also be pretty long. A recent study conducted by Dan Misener of Pacific Content reveals that “Half of all podcasts use less than 163 of the 4,000 characters available.” This seems to be a huge waste of the potential for podcast apps, Google, and all search engines to see what your podcast episode is about. Take your episode descriptions up a notch by making them longer.
Should You Add Show Notes to Your Episode Description?
One simple way would be to post show notes within the podcast description. However, one of the main appeals for show notes is that it provides a reason to push listeners to your website where you can track their visit, ask them for an email to grow your newsletter, and send them to your social media. For that reason I recommend writing a separate long-form episode description, or simply excluding part of your show notes so you can still push listeners to your website.
Properly Format Your Episode Descriptions
Make sure to properly format your episode descriptions using basic HTML. Remember that just because your episode description looks good in your podcast host (eg Buzzsprout) doesn’t mean that it will look good on an iPhone X in Apple Podcasts.
Episode Artwork
Another way to improve your podcast SEO is to create episode-specific podcast art. Although this isn’t supported by all podcast directories yet, it is becoming increasingly popular. Spotify, for example, shows your episode specific artwork in their mobile app. This creates a more exciting experience for your listeners and increases the clickability of each episode.
3. Social Media
Developing a social media strategy for your podcast is a powerful way to drive listeners to your podcast. Stay active on social media and post every time you release a new episode.
If you’re not convinced of the value of social media, take a look at these user stats:
Instagram has 1 billion monthly users
- Facebook has 1.56 billion daily active users
- Snapchat has 186 million daily active users
- Twitter has 126 million daily active users
- Instagram has 1 billion monthly active users
- Tik Tok has 800 million monthly active users
Given the size of these platforms, it’s clear that they are a critical part of marketing your podcast to the world. Each social platform has its own unspoken rules and expectations, and if you can learn how to optimize your content between each platform you will boost your engagement and impact.
Where Should I Post About My Podcast?
There are more social apps than ever before and there are major shifts in the social landscape all the time.
Whether it’s the innovation of stories on Instagram, Facebook, YouTube, and now Twitter , or the development of new apps like Tik-Tok, it is hard to keep up with all of the changes!
You don’t need to be on every platform, but the more places you can promote your podcast the better.
While I definitely recommend posting your content on as many channels as possible, I’m also a realist. You can’t be everywhere and you can’t do everything. More than that, your target audience probably spends more of its time on one or two of these platforms listed below.
Once you do some preliminary research and figure out where your podcast listeners hang out, you can start implementing the strategies below.
Audiograms
Audiograms are short video clips (usually with a waveform or transcription) from your podcast that you can easily publish across social media platforms (and YouTube, if you like).
They provide immediate access to the content within an episode of your podcast so potential listeners can know what to expect. Ideally, they will drive listeners to listen to a full episode and subscribe to your podcast from there.
The other benefit of audiograms is their shareability. You can easily tag your guests and ask them to re-share the content on their social pages or send it directly for them to publish on their own feeds.
Social Cards
Similarly to audiograms, social cards share a key quote from your podcast episode to show potential listeners what they can expect. They are shareable and engaging.
Engage Others On Social Media
Social media is just that: social. A large part of effectively marketing on social media is just being human and connecting with other people in the comments section. So take the time to sit down and study the market, and take part in the conversations happening on your posts. This strategy, or etiquette really, is true for every single social platform. However, not all platforms are created equal in this regard. Twitter is far more comment and conversation-focused than Tik-Tok. But Tik-Tok is far more video-driven than Twitter.
Gary Vee does this really well.. He emphasizes the importance of listening to your audience before you create content.
He frequently recommends building your brand by spending a few hours every day simply researching hashtags, geo-tags, and people and dropping intentional and positive (non-spammy) comments. He calls this strategy the $1.80 Cent Strategy.
This is a less-than-inspiring strategy because it requires getting your hands dirty in some busywork but he really pushes this strategy and his own platform is evidence of the potential for success.
Repost Other Relevant Content
Take your social media strategy up a notch by sharing more than your own content. Don’t just post when you drop a new episode of the podcast, but also make sure to invest in your audience by reposting other content that is relevant within your niche.
The $1.80 Strategy (Instagram)
The $1.80 strategy from social media marketing expert and influencer, Gary Vaynerchuck, is a method for boosting engagement on your social media and getting more followers.
The strategy is to look up the top 10 hashtags in your respective industry and to leave your “two cents” in a comment on each of the top 9 posts. Let that sink in, Gary is suggesting that you take the time to like and comment on 90 posts every single day. Social media isn’t an easy game. And Gary really does believe that it’s a volume game, so if you want to win you’ve got to put in the hours.
And you don’t just have to search through the top hashtags. You can also use the geotag tools and look up your city, or a city that you’re trying to target, and comment on the top photos in your location of choice. You can watch Gary’s explanation of how this process works here.
4. Podcast Websites

Podcast websites act as a home for your podcast brand, bringing together all the different marketing efforts to one location. These sites typically feature embedded episodes, show notes, transcripts, bonus content, links to all of your social media, and a way to sign up for an email newsletter.
A website can act as a house to store all of the other marketing channels for your podcast.
Learn More
How to Create a Stunning Podcast Website
5. Email Newsletter
Building an email subscription list is a powerful way to market your podcast every time you drop a new episode. Email marketing is a great way to build your brand because email isn’t going away anytime soon.
As you build your email newsletter, focus on the quality of your content. We all know how annoying spam email campaigns can be, so make sure that you really add value for your readers. Apply the golden rule to your email marketing campaigns and only send emails that you would like to read yourself. Serve your audience with high-quality content and don’t spam them with wasteful emails.
Apply the golden rule to your email marketing campaigns and only send emails that you would like to read yourself. Serve your audience with high-quality content and don’t spam them with wasteful emails.
At Resonate we use Mailchimp to manage our newsletter “Amplify”. It has been highly reliable, easy to learn and use, and has a super in-depth knowledge base for troubleshooting issues.
And your newsletter doesn’t have to only be published when you drop an episode of your podcast. For example, Tim Ferris has a series he calls “5 Bullet Fridays” where he shares strange and interesting things he is reading, watching, or experimenting with. Add variety to your email campaign to keep your audience engaged. Just make sure you’re always adding true value.
6. Online Communities
Facebook and Reddit groups can be excellent places to get your podcast in front of the right audience. You just have to be careful because some groups prohibit you from posting about your podcast or brand, but other groups gladly allow you to self-promote.
You should join as many of these communities as possible. Listen and learn about the community you are serving, even if you aren’t allowed to directly market your podcast or brand. A simple search for “Podcast” on Facebook groups brings up dozens and dozens of niche groups within the larger podcasting community.
The other benefit for joining these groups is that it keeps you relevant. Take note of the concerns, questions, and topics that people are discussing. This is a great way to think up future content for your podcast.
7. Guest Appearances
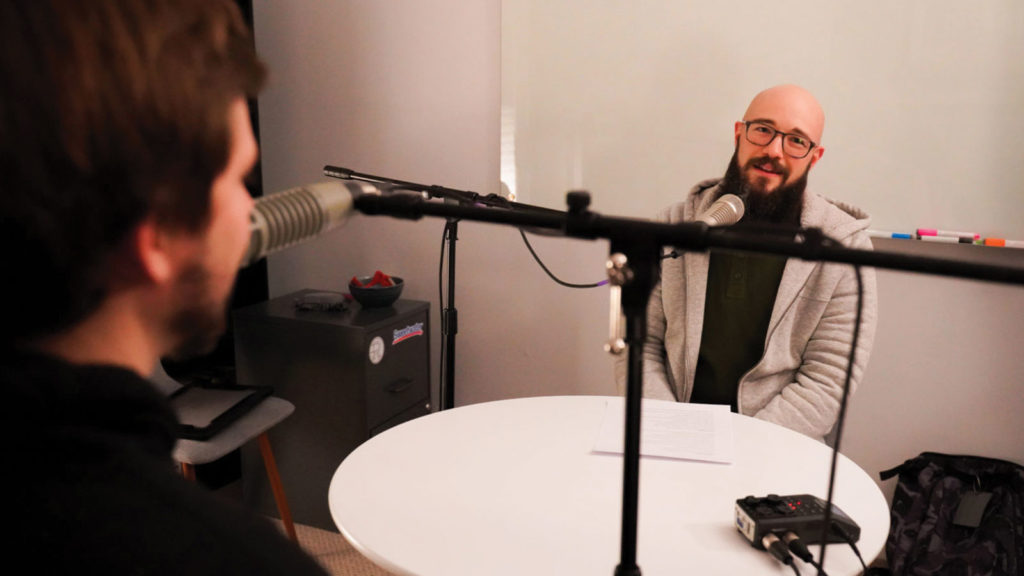

Showing up as a guest on someone else’s podcast is one of the most powerful ways to promote your own brand. It can help establish you as an expert in your field and broadens your reach by putting your voice in front of a whole new audience of listeners. Trading interviews or being a one-time guest on another podcast is a great mutually beneficial way to promote your podcast and your friends.
One great thought is to consider interviewing other podcasters with greater followership & influence than you. Look at where others are, where you want to be & see how you can bridge that gap with their help. There’s no shame is being honest & asking for some assistance. Most podcasts have been helped along the way as well & they are readily available to lend a helping hand. This is the case not only with interviews but also with cross-promotion & marketing through ads.
Have a podcast you like? Ask them if they’d be willing to do a little promo for you in exchange for promoting them. Use the success of others to your own advantage. Look for the success of others as a way to help yourself learn & grow.
You can use the free tools on Podchaser to research other shows in your niche, by finding lists of podcast recommendations and cold-emailing hosts. But if you want to go a step further, and find podcast placements in a particular niche or industry, you should check out their beta program Podchaser Connect.
Appearing as a guest on other shows is a strong way to organically promote your podcast, gain experience as a host, and expand your reach. But the same is true for hosting other guests on your own podcast.
By hosting engaging conversations with experts in your field, you increase your credibility, boost engagement, and can better serve your listeners. We recommend hosting guests on your podcast as well as building relationships that allow you to guest appear on other relevant podcasts.
8. Grassroots Podcast Marketing

What’s more powerful than hearing a personal recommendation from someone that you trust?
Never underestimate the power of sharing your content with your existing network of friends and family, and your local community.
Several ways to promote your podcast locally include finding local podcast meetups or conferences in your niche, sharing your podcast directly with your friends (text, email, in conversation, etc), adding a link to your email signature, etc. Don’t be overly pushy, but don’t be afraid to show your podcast either!
9. Paid Podcast Promotion
If you really want to take it to the next level, consider paying for initial advertising. Also, spend some time on keywords to target that will reel in the listeners you believe will be drawn to your podcast. Keep it simple & logical. Use those keywords in your descriptions & show notes, but don’t stop there. Once you’ve figured out what keywords to target, consider paying for paid advertising on Google Adwords, Reddit Ads, and Facebook Ads—at least as a temporary measure. Your first listeners are going to be the hardest to get, so it’s worth the money you’ll spend to net early listeners if you can afford it.
There are several factors to consider when asking whether you should use PPC in your marketing strategy. The main question is what is your budget? One recent study revealed an average cost for gaining one new listener was $4.31. He showed that it would take 172 ads (at the current CPM of $25) to simply break even in this ad campaign conducted on Google Search.
Now, this test was only run on a single podcast, but the evidence seems pretty strong against the use of PPC for podcast advertising at this stage in the industry, from a strictly monetary standpoint. However, like we said, it might be worth gaining initial listeners for your podcast, even if you lose a little money.
It might be that you discover your target audience is more receptive to paid ads and yields a much more affordable ppc rate. Time will tell if this method of marketing is truly worth implementing.
Best Free Marketing Tools
1. Canva (Graphic Design)
Canva is a free online graphic design program. This software is available for free, although some features require a monthly subscription. It’s a powerful tool for creating simple social content for your podcast. What’s even better is the story behind it. Canva was created by Melanie Perkins when she was just 19 years old. Incidentally, you can hear the story of how she created Canva, this industry-disrupting tool, on the How I Built This Podcast with Guy Raz.
What I like about Canva:
- Intuitive drag-and-drop interface
- Easily customizable templates
- Simple and clean user interface
- Stay organized with design Folders
While the essential aspects of Canva are available for free, there are also a number of incredibly handy features that require a paid membership.
2. Headliner (Video Editor)
My second favorite free marketing tool is Headliner, the free video-editing software. Your marketing efforts are all but lost if you are not creating content for social platforms. This is an incredible tool for creating engaging social media content.
There are 4 key tools that Headliner provides.
- Audiograms
- Article-to-video conversion
- Transcriptions
- General Video Editor
All four of these features on Headliner are totally free. The two best features are definitely the audiogram and transcription tools.
The audiogram wizard generates a WAV file that matches your uploaded audio. This is a great way to give your social media audience a taste of your podcast’s content in a more engaging way than a simple video.
Headliner’s transcription tool, while not the best on the market, is excellent for transcribing short audio clips. I cannot emphasize enough how important embedding transcriptions in your video is right now. And this tool is a great way to make your content that much more engaging, for free! Don’t believe me? Influencers like Gary Vee are really trumpeting the power of transcription. Look at Gary’s Instagram and see how engaging each post is!
If you are looking for customized audiogram designs, check out our podcast marketing services.
3. Google Alerts (Keyword Monitor)
A major aspect of every marketing and content planner’s job is just keeping up with the times. Obviously, this requires that you stay up to date on the latest Twitter beef, Instagram memes, and flourishing Facebook groups in your respective industry. In many ways this can be a full-time job in itself. But in order to keep up with blog posts and longer form mediums, I like to use Google Alerts.
Google Keywords allows you to track specific keywords relevant to your industry and interests. You can set up the tool to send you a daily/weekly email alert to summarize the keywords you are tracking, or you can even add the RSS feed of that keyword to a channel in Slack for monitoring your blogs. This tool is invaluable to me as I try to keep a pulse on the latest news in the podcasting industry for Resonate’s Podcast Pro Weekly. I highly recommend this free marketing tool.
An alternative tool that I have used in the past to curate content is Feedly. There are a number of content curation tools like this that allow you to track keywords and topics, but I have found Google Alerts to be the most effective tool for me.
4. Pocket (Cloud-Based Swipe File)
Following up on the content curation tool Google Alerts, I wanted to highlight this helpful Google Chrome plugin called Pocket. As the name suggests, Pocket is a fast and easy way to store digital content for later.
Every creative needs a swipe file, and Pocket is a wonderful tool to use as a swipe file on Google Chrome (or any browser compatible with Chrome Web Store plugins). It also has an app for Apple and Android and automatically syncs across all platforms.
See an article or video you like? Install the Pocket plugin then just click the arrow at the top right of your browser to save it for later. It’s that easy.
5. Chartable Smartlinks
Chartable Smartlinks are a powerful tool for studying your podcast audience. They offer two important features:
- A linktree for users to subscribe to your podcast on their favorite app (Apple, Spotify, Google, etc)
- Tracking where your listeners came from to download your show (eg Instagram or Facebook)
Using a smartlink for your podcast streamlines the process for your listeners to subscribe to your podcast on their favorite app, while simultaneously letting you track which social media platforms are converting the most listeners for your podcast.
Tracking Your Growth
Tracking your podcast’s growth requires pulling data from several different platforms, including your podcast hosting dashboard, Apple Podcasts Connect, Spotify for Podcasters, and Google Podcasts manager.
You should also pay attention to your social media analytics on Instagram (make sure you have a business account), Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. If you have a podcast website, you can link your site to Google Analytics to pull in-depth analytics about your users and their activity. I highly recommend using Chartable Smartlinks (listed above) to track where your listeners are coming from.
Conclusion
As you market and track your podcasts, remember that it is a long-term game. Don’t expect your podcast to become an instant hit overnight. Work hard, serve your audience well, and your audience will grow in time.
I hope this blog helps you grow your podcast audience. Have further questions, suggestions, or ideas? Send me an email and let me know what you liked and how we can keep making our content more helpful!












